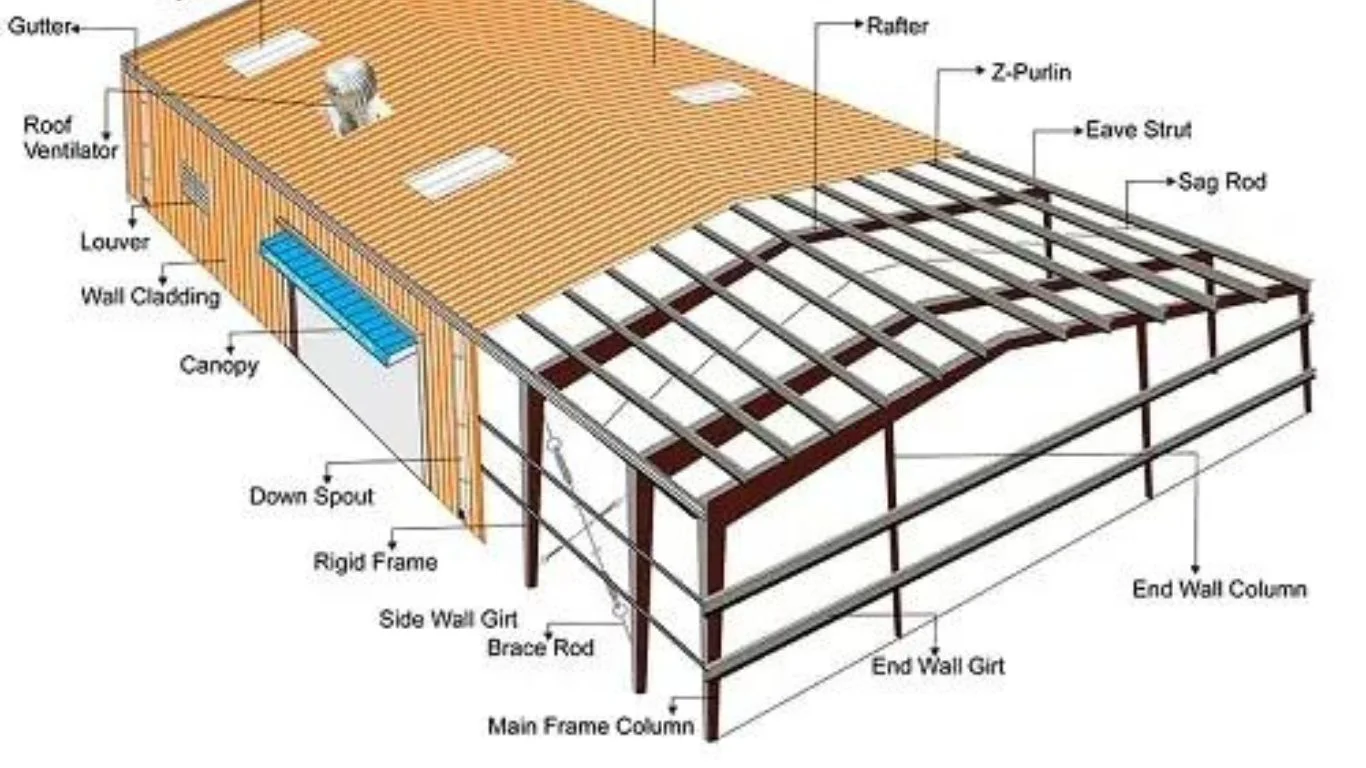
Understanding the Role of Purlins in Pre-Engineered Buildings (PEB)
Pre-engineered buildings (PEBs) rely on steel purlins as essential secondary support structures. These elements help distribute the load of the roof and deck while reinforcing the building’s overall structural integrity. Positioned parallel to the building’s eaves, purlins are supported by rafters or walls and contribute to the stability of the roof framing.
Typically made from cold-formed steel, purlins can span up to 30 feet or more, depending on the building’s design requirements.
Their dimensions are influenced by factors such as the primary frame size, building usage, and structural engineering calculations. If necessary, purlins can be reinforced to prevent structural weaknesses, making them a vital part of PEB construction.
Types of Steel Purlins in PEB Structures
Steel purlins are commonly used in various pre-engineered buildings due to their lightweight nature, durability, and precise manufacturing. They also expand in warm weather and contract in cold conditions, adapting to temperature variations without compromising structural integrity. The two most common types of purlins used in PEB construction are:
1. C-Shaped Purlins
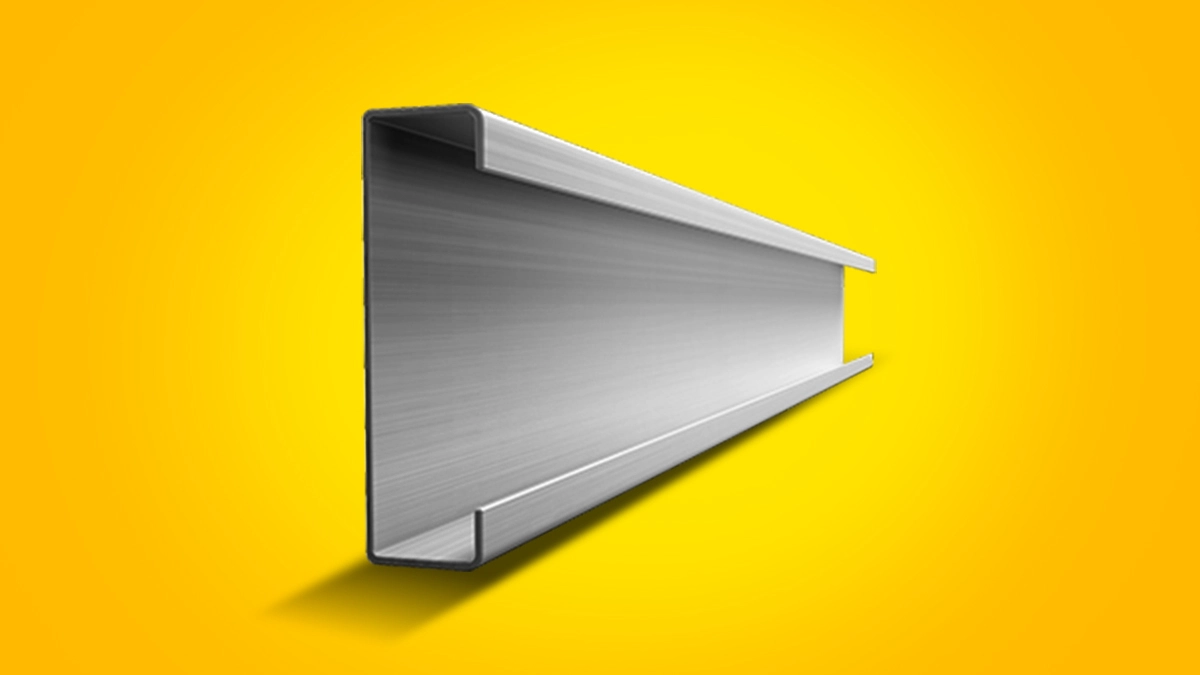

C-shaped purlins, as the name suggests, resemble the letter ‘C’ and are primarily used for supporting walls and flooring. Depending on their design, they may be classified as:
U-Section Purlins: Do not have flange stiffeners.
Channel Section Purlins: Feature flange stiffeners for enhanced strength.
C-purlins are symmetrical in shape, making them ideal for easy transportation and storage. However, due to their structure, they cannot be lapped, meaning they are typically used in clear span designs where stability is a priority.
2. Z-Shaped Purlins
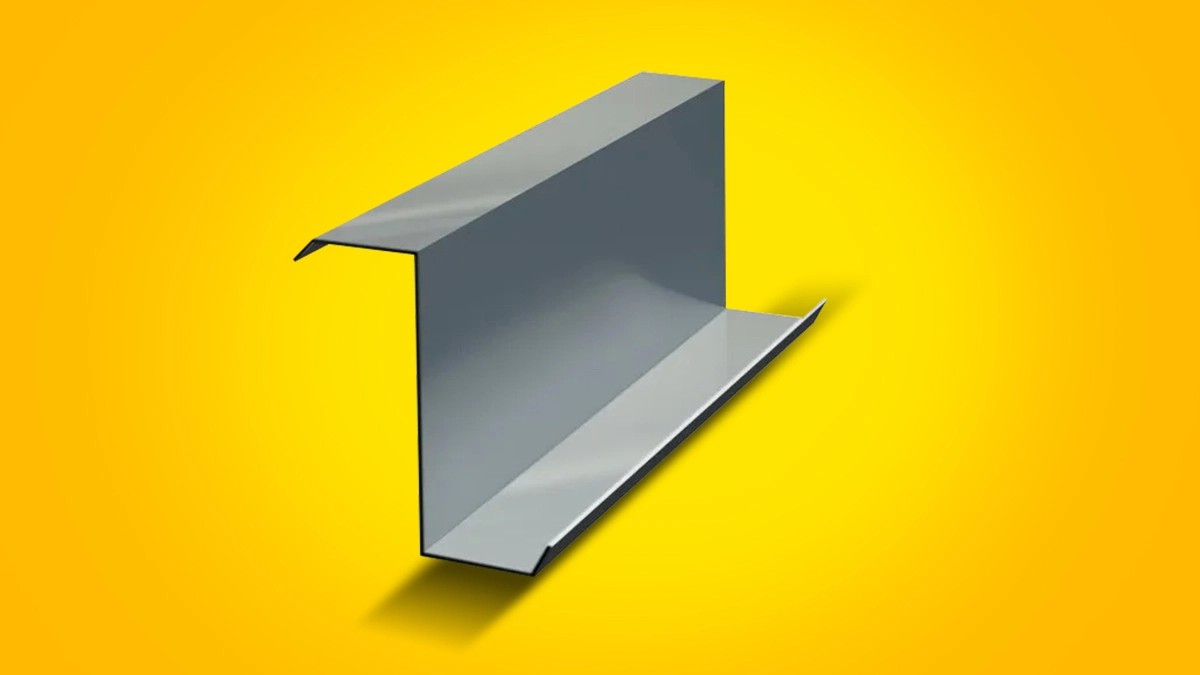

Z-shaped purlins are more robust and widely used for structural reinforcement. Their unique shape allows them to be overlapped, providing additional strength in areas requiring load distribution. These purlins are placed between the roofing sheet and the walls, ensuring proper support for the major structural framework.
The ability to lap Z-purlins by rotating them 180 degrees and fitting them together makes them a preferred choice for roofing applications that demand enhanced load-bearing capacity.
Preventing Structural Instability in Purlins
Purlins and girts can experience lateral instability, which may cause deflection and rotation. Engineers use techniques such as bridging and fixing sheets with screws to counteract these issues. By applying proper bridging, free flange lateral deflection and section rotation can be minimized, ensuring a more stable structure.
Conclusion
Purlins play an indispensable role in PEB construction by supporting the primary frame and ensuring the structural integrity of the building. Their lightweight yet durable design makes them an essential component for modern industrial, commercial, and residential structures. Choosing the right type of purlins, along with proper installation techniques, helps improve the overall efficiency and longevity of a PEB.
For expert guidance on PEB construction and structural solutions, contact EPACK Prefab. With over 25+ years of experience and 100+ ongoing projects across India, we are committed to delivering top-quality prefabricated building solutions. Reach out to us at enquiry@epack.in or call +91 8130444466 to discuss your project requirements.